Causes And Treatments Of Skin Cysts
It is not uncommon to see bumps or bumps on the skin at some point in life. Many of these are skin cysts, and patients typically consult to determine if they are abnormal or dangerous.
The truth of all is that these formations are usually benign in most cases and do not carry complications. Even, as detailed in an article published in the National Health Service (NHS) , many disappear without treatment. What are its causes?
What are skin cysts?
Skin cysts are dome-shaped bumps, filled with fluid, air, or other matter, found just under the skin. There are different types, but they are often benign or non-cancerous. .
There will be situations where it is difficult to tell with the naked eye whether a lump is a cyst or something else that may need treatment. Tests, such as a CT scan, ultrasound, or histopathologic biopsy, may be needed to confirm the diagnosis.
Therefore, in the presence of any lump, it is advisable to go to the family doctor to carry out the corresponding examinations. Once this is done, it will be the professional who determines if it is necessary to adopt measures to eliminate it.
As with other types of cysts in the body, the cutaneous ones vary in size, from a few millimeters to a few centimeters. They grow slowly, they do not hurt, but they can become tender and painful if they become infected. If so, its coloration also changes and a surface reddish and hot, or yellowish white.
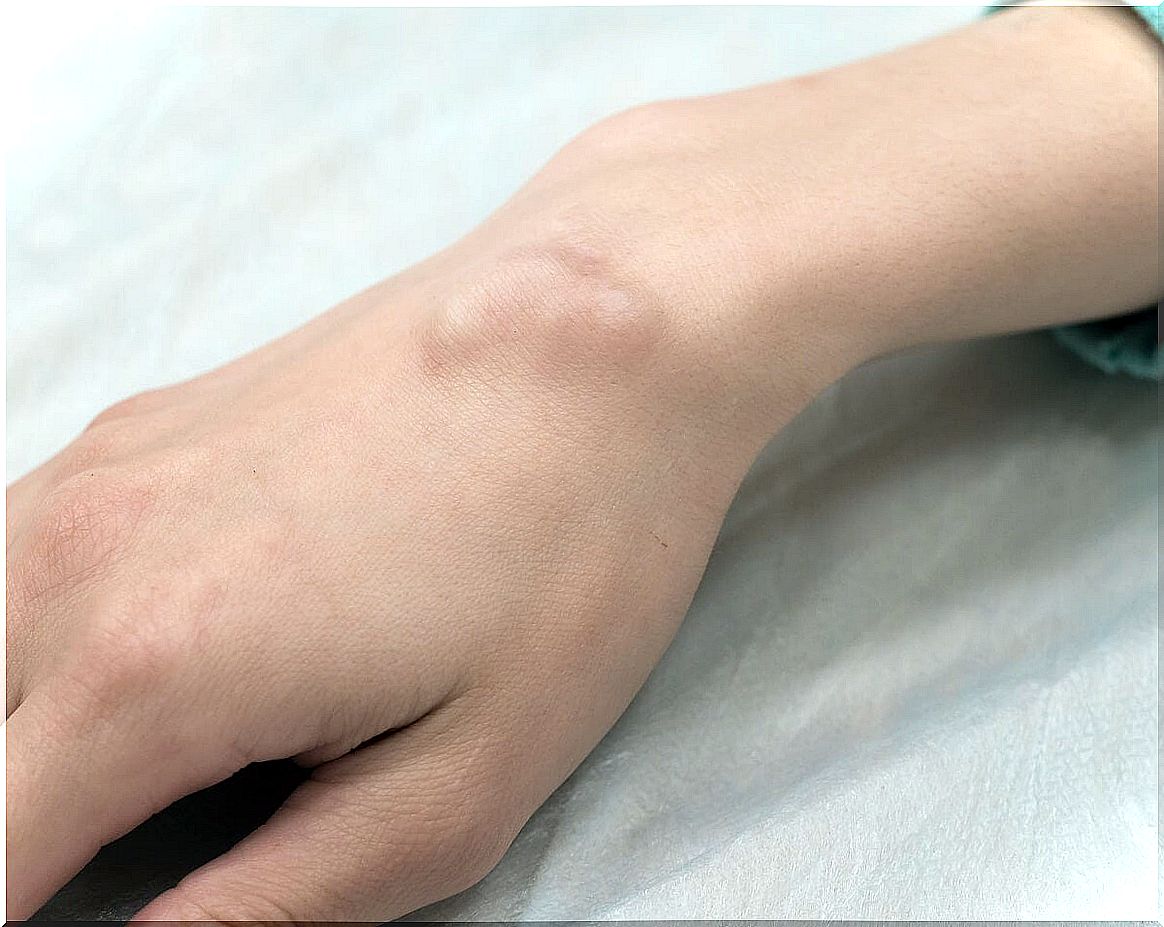
Most common types of skin cysts and treatment
As detailed in a publication in the European Journal of Radiology Open , several types of skin cysts have been defined whose content of fluid or semi-solid material causes them to protrude in the skin. They, in turn, have several characteristics and possible causes.
Milium or milia
These types of cysts are tiny and appear as hard white papules, 1 to 2 millimeters long, usually located on the face. It can occur at any age, even in newborns. Its treatment is done for cosmetic reasons, with topical retinoids or through a surgical procedure. They are benign in character.
Epidermoid cysts
Sometimes misnamed sebaceous cysts, they are the most common skin cysts to observe. They occur anywhere on the body, but are most commonly seen on the face, the base of the ears, the trunk, or the genitals.
They are shaped like skin-colored nodules; in addition, its size can be from several millimeters to several centimeters. They also tend to become inflamed, red, and painful if they become infected or ruptured. Some of these cysts can be fluctuating.
A proper diagnosis requires a histological examination. Although they improve without treatment, they can be eliminated more quickly through a local corticosteroid injection or surgery.
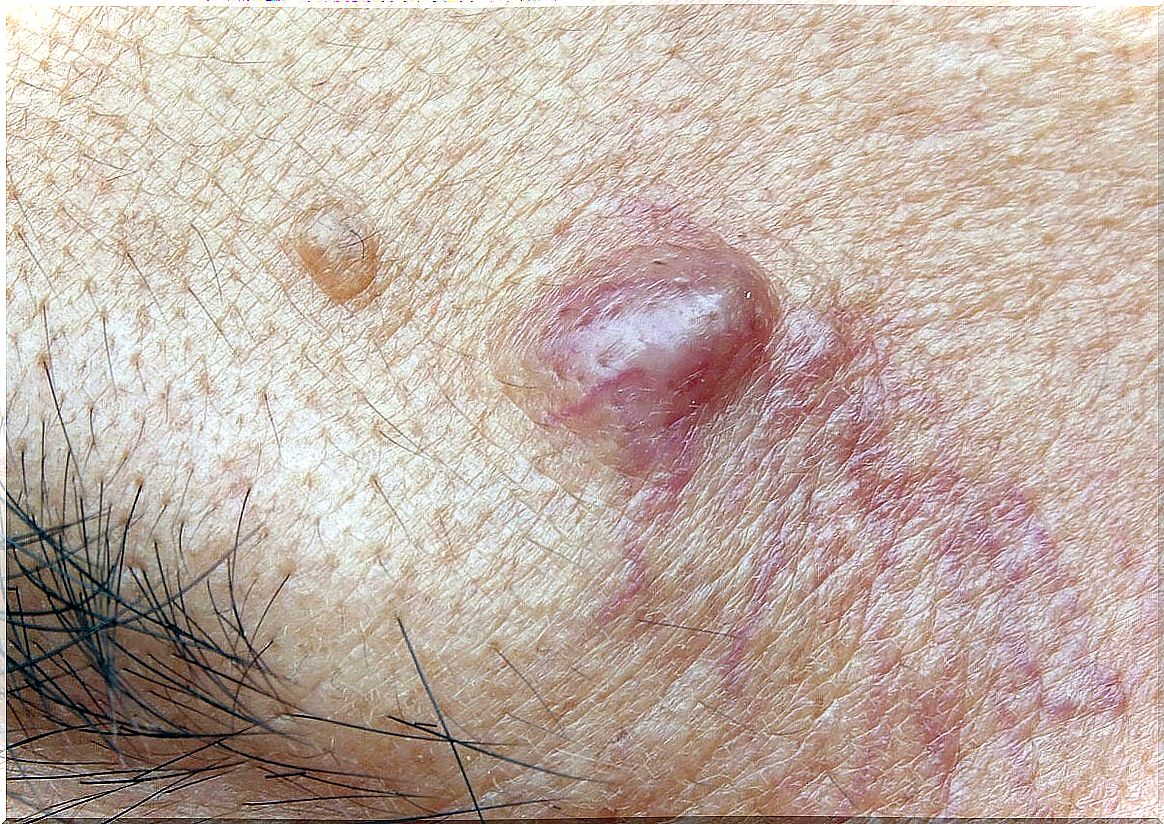
Trichlolemic cysts
They are subcutaneous (deeper) nodules, firm and slow growing. They are most often located on the scalp. Sometimes a hereditary history is seen. Histological examination will be carried out for its accurate diagnosis and, later, they are treated through a surgical incision.
Hair cysts
They occur in children and young adults. They are characterized by a sudden appearance of small dome-shaped follicular papules, usually on the trunk. Its evolution is slow, it can regress spontaneously. If treatment is required, it will be surgical, or with a carbon dioxide laser or topical retinoids.
Multiple steatocystoma
Multiple steatocystoma is rare. It is characterized by multiple cysts that contain sebum and measure from 2 millimeters in diameter to 3 centimeters or more. P They can manifest in any part of the body, but show a predilection for the thorax.
Treatment is often difficult due to the large number of injuries. Options include surgical treatment and carbon dioxide laser therapy.
Why do cysts form?
Anyone can develop a skin cyst, they are not contagious and are usually harmless. They are formed from the outermost skin layer, called the epidermis, or from the epithelium of a hair follicle.
Small cysts that do not cause any problems can be left to their evolution. Some even disappear without treatment. If you are infected, there is a risk of spreading the infection and will require antibiotic treatment. Therefore, it is suggested to consult your family doctor.
In case of treating them with a surgical procedure, it must be considered that this procedure can leave a scar; in addition, it is possible that they grow back.
Although its differential diagnosis will be made mainly by the location, evolution and history of the patient, many times it will be necessary to do a biopsy with a histological study, in order to make an unequivocal diagnosis. In the presence of pain, rapid growth or discoloration, an evaluation will be necessary.