Infantile Hemangiomas, What Are They?
Infantile hemangiomas are relatively common. Therefore, it is necessary to know what they are and how to treat them.
Infantile hemangiomas are generally benign tumors. They are characterized by the proliferation of blood vessels in an abnormal way. They are usually located on the skin, although they can also be found in other organs. In this article we explain what they are and what to do about them.
What are infantile hemangiomas?
They are tumors, as we have already said, generally benign, which usually affect the skin. It is one of the most frequent neoplasms in infancy and childhood. In addition, they affect three times more women than men. They are usually located on the face or scalp.
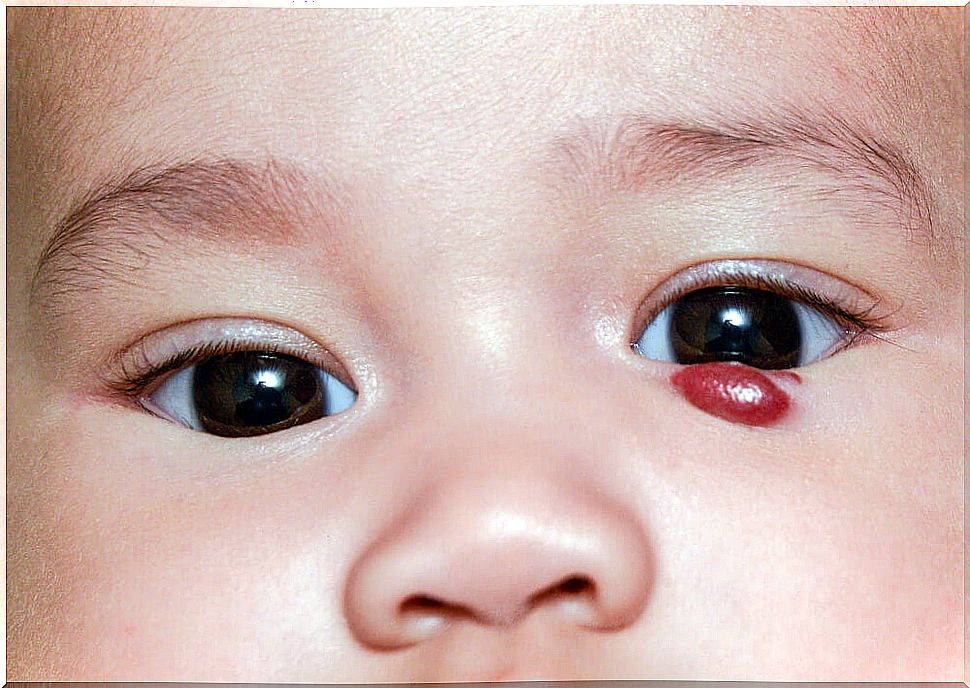
Although most infantile hemangiomas are benign, some of them lead to complications. These are flat or raised reddish tumors that affect aesthetically in the first place. In addition, they can compress neighboring structures such as the eyes, nose, mouth, and so on.
Infantile hemangiomas present a pattern of evolution. They have a first phase in which there is rapid growth, rapidly increasing their volume and size. Then there is a resting phase, in which the hemangioma changes very little.
Finally, there is a phase of involution in which it begins to disappear naturally. However, it is advisable to intervene if they are large or if they cause complications.
Why do infantile hemangiomas occur?
The exact reasons for their formation are not known. However, a number of risk factors have been discovered that could be related to the development of infantile hemangiomas.
In the first place, Spanish researchers from the Hospital La Paz in Madrid affirm that the lack of oxygen in the placenta during the first months of gestation could produce alterations in the placental circulation. This alteration could be related to hemangiomas.
Other studies link infantile hemangiomas with advanced age of the mother and multiple gestation. Similarly, they are related to placenta previa and pre-eclampsia. It has been seen that the more premature the baby is, the more likely it is to develop a hemangioma. For this reason, the researchers associate the lack of oxygen with its development.
Types of infantile hemangiomas
Infantile hemangiomas can be cutaneous or internal. In general, they are usually classified according to:
- The depth of the affected vessels: they can be superficial, deep or mixed. The superficial ones are usually bright red papules. In contrast, deep ones are bluish or skin-colored lumps.
- According to their shape and distribution: they can be focal, segmental or multiple.
Diagnosis
Most are diagnosed by a physical exam. A complete medical history is necessary. Pregnancy data, the perinatal period and the evolution of the lesion must be detailed. Most infantile hemangiomas start out as pink or pale spots. Therefore, they can be confused with nevi, trauma or malformation.
Complementary techniques can be performed for diagnosis. These include ultrasound, magnetic resonance imaging, and skin biopsy. Skin biopsy is the most indicated to differentiate them from other lesions.
Complications
The most typical complications are usually at the local level. Cutaneous infantile hemangiomas can ulcerate. This increases the risk of infection, as well as causing pain. When hemangiomas are found near the eye, they can alter vision, causing astigmatism, strabismus, and even vision loss.
However, the most important complication is the possible psychological impact. Infantile hemangiomas in visible areas damage a child’s self-esteem. This is because they are visibly unsightly. In fact, some of them tend to scar.
Treatment

Not all infantile hemangiomas need to be treated. The indication for treatment is complex. However, it is indicated when they are life threatening, when there is ulceration and pain or when there is a risk of permanent scars.
The treatment of choice is oral propanolol. It is a beta-blocker drug that, although effective, has numerous side effects. Among them stand out bradycardia, hypoglyclemia, affect the mood and sleep, and so on.
Another possible treatment is interferon alpha. However, it can cause serious complications in infants. Laser treatment can also be helpful. The surgeries are primarily indicated in the treatment of sequelae. However, with the use of propanolol the sequelae have been markedly reduced.
In conclusion
Infantile hemangiomas are a relatively common health problem. It is necessary to consult the doctor in case of any doubt. In the same way, the psychological repercussions that they can have on the child must be taken into account in order to improve the treatment.