Skin Tags: Causes And Risk Factors
The presence of skin tags should not be a cause for concern, as these are harmless injuries. If you choose to remove them anyway, it is appropriate to put the case in the hands of a dermatologist.
Skin tags are bumps that grow on the skin in different areas of the body. They are initially small and shaped like a flattened pinhead. They are brown and can grow up to 5 centimeters.
There are many people who mistake skin tags for warts because they look similar. However, while warts are soft, smooth, and rise above the skin, warts are rough, hard, and have hardly any volume.
Also known as soft fibroids , they are not contagious. Some types of warts are, when they are caused by the human papillomavirus (HPV). What they do have in common is the fact that they are benign skin lesions.
Causes of skin tags
Science is not clear about the reasons why skin tags appear. These occur most often in areas where the skin folds, such as the neck, armpits and groin. They are also found on the face, especially the eyelids.
Therefore, it is believed that the possible cause of these bumps is skin-to-skin rubbing. The idea that they are linked to the human papillomavirus is not ruled out, but there is insufficient evidence for this.
It is also possible that they arise based on a certain genetic predisposition, since they have been found present in members of the same family.
Symptoms of skin tags
Skin tags have the appearance of a hanging mole, although they are usually darker in color. They are detected with the naked eye, but sometimes a biopsy is required if there are doubts about the diagnosis.
Typically, these soft fibroids do not cause any noticeable symptoms. Discomfort may arise because they catch on clothing or become irritated by rubbing. If the stem is twisted, it is possible that they become necrotic (the tissue dies). This causes pain, inflammation and the risk of superinfection.
Risk factor’s
It has been detected that this type of fibroids are more frequent in males and that they rarely appear before the age of 30. The highest incidence occurs after age 50 and cases increase simultaneously with age.
In addition to age and gender factors, there are other conditions that appear to be related to the appearance of skin tags. Among them are the following:
- Obesity.
- Pregnancy.
- Acromegaly or gigantism.
- Insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes.
- Crohn’s disease.
What treatments exist to remove them?
In principle, skin tags do not require any treatment, as they do not pose a health risk. However, some people feel the need to remove them for discomfort caused by rubbing or for cosmetic reasons.
Depending on each case, there are several alternatives to achieve the task of eliminating them. Among the techniques are the following:
- Ligation: it is a manual technique that consists of tying a piece of suture thread at the base of the skin tag, so that circulation is cut off. The thread is left there for several days. The lesion dries up and sloughs off on its own.
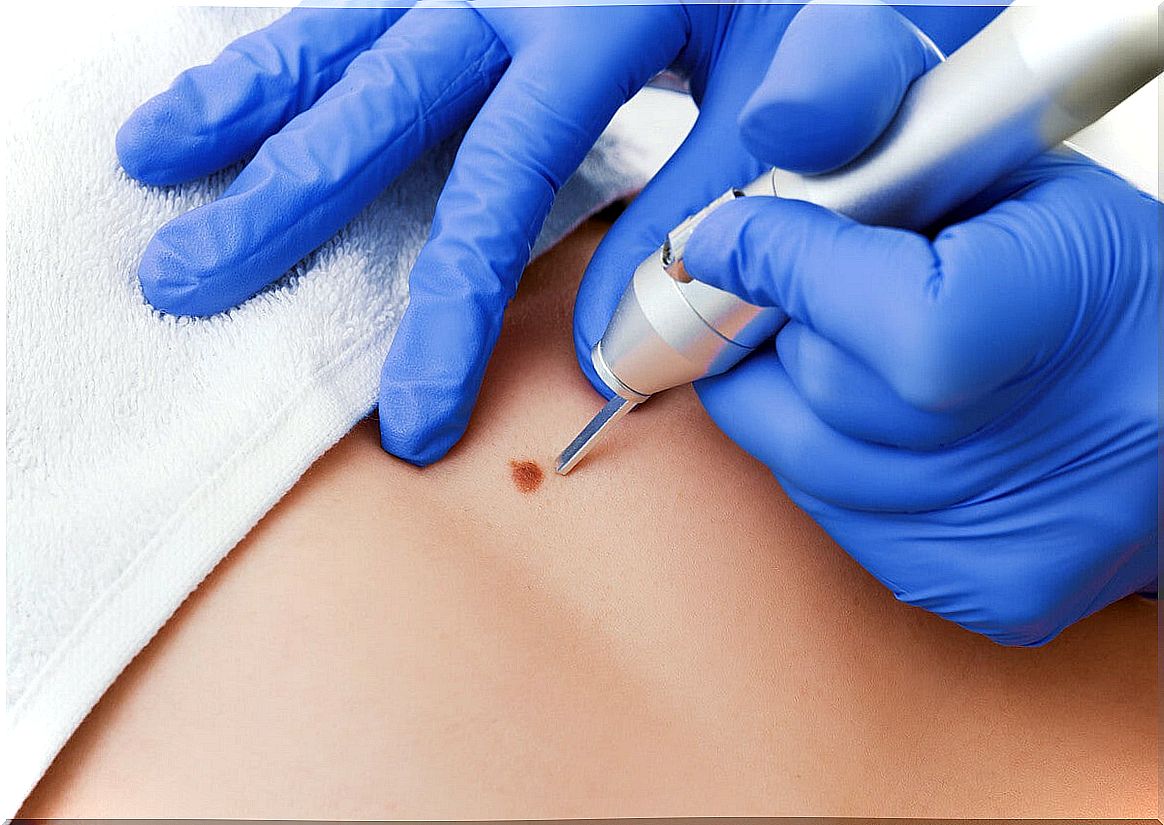
- Surgical removal: it is done using forceps and scissors. It usually requires local anesthesia and silver nitrate to control bleeding. If the injury is very large, it requires suturing.
- Cryotherapy : This is a method in which liquid nitrogen or argon gas is used to create intense cold. In this way the lesion is frozen and removed. It is the most used technique in dermatology.
- Electrosurgery: it is minimally invasive and consists of applying electrical current to the lesion to burn and detach it. It is faster than other methods, causes less bleeding and guarantees good asepsis.
- Fractionated CO2 laser: this is one of the most modern systems. It is performed under local anesthesia and uses tiny beams of light. These form tiny cuts and allow the skin tag to come off.
Skin tags are benign
Skin tags may look strange, but they are actually harmless. Some people use anti-wart fluids to remove them, although this is incorrect as this is a different lesion.
It is important to clarify that, although the ligation method is simple and apparently within the reach of anyone, it is best to have it carried out by someone trained for the purpose. Otherwise unnecessary complications may arise.
Even though skin tags are a benign lesion and not dangerous, it is ideal to put the situation in the hands of a dermatologist. This is the competent professional to evaluate it and decide what to do.