What Is Epiglottitis And How Does It Occur?
Epiglottitis is a disorder that occurs when the epiglottis – a flap of cartilage located in the throat, behind the tongue, and in front of the larynx – becomes inflamed and obstructs air flow to the lungs. Mortality in this clinical picture is 2-3%, even with emergency treatment.
According to bibliographic reviews, it was estimated that 14 out of every 100,000 inhabitants suffered from it. Due to vaccines and other preventive measures that we will cite later, the current incidence is 2 to 3 cases per 100,000 people. If you want to know more about epiglottitis, keep reading.
Common symptoms of epiglottitis
As we have already mentioned, the swelling of the epiglottic organ and the arytenoid muscles prevents the entry of air into the upper respiratory tract. According to the Mayo Clinic, some of the most common symptoms of this event are the following:
- Fever.
- Severe sore throat
- Muffled or hoarse voice
- Abnormal sound when inhaling.
- Drooling, pain, and difficulty swallowing.
The symptomatic course in adults can develop in a matter of hours or days, while children worsen more quickly. This assessment is necessary, since the vast majority of epiglottitis cases occur in infants between 1 and 6 years of age.
Unfortunately, as indicated by the MSDmanuals portal , some of the children with symptoms of epiglottitis have bacteria in their bloodstream (bacteremia). This situation is serious, as the infection can spread to the heart, meninges, lungs, or joints.
Main causes of epiglottitis
Epiglottitis can appear from two main causes: infectious or traumatic. Below we break down each one of them.
1. Infections
According to the journal Family Medicine, up to 90% of epiglottitis cases are due to infection with Haemophilus influenzae type b (Hib), an opportunistic bacterial pathogen that attacks the patient when their immune system is weakened. Other bacteria that can cause the disease are Streptococcus pneumoniae and Staphylococcus pyogenes .
In general, the Hib bacterium lives as a commensal on body surfaces, but in the face of another pathology or a concomitant infection it can take advantage to invade tissues that would not be vulnerable. Once settled in the respiratory tract, the bacteria can be transmitted with the cough and sputum microparticles of the patient.
Herpes simplex or varicella-zoster are viral pathogens that can cause the disease in a few cases.
2. Trauma
A very strong direct blow to the throat can cause epiglottitis, as inflammation of the tissue involved also occurs in response to injury. The patient will experience similar symptoms in the following events:
- Ingesting a chemical compound that causes burning or corrosion of the throat.
- Ingesting a foreign body.
- Smoking drugs, like crack .
Available treatments
According to the Healthy Children portal , the first thing to do is call the emergency room and, while waiting for the professionals to arrive, try to calm the patient. They should not be asked to lie down or drink water, as this can make the condition worse.
Depending on the severity of the infection, an intubation of the patient may be required to help him breathe, contemplating in some cases the tracheostomy. The essential thing is that the patient breathes again at all costs and, once this is achieved, broad-spectrum and specific antibiotics can be prescribed to combat the causative bacteria.
Risk factors and groups for epiglottitis
As we have said, children between 1 and 6 years old are the most likely to present this clinical picture, since their immune system is not yet ready to fight certain infections. According to the aforementioned portals, some of the risk factors are the following:
- Being a man: Epiglottitis is more common in men than in women.
- Have a weakened immune system: our immune system is an excellent barrier against most of the pathogens that cause epiglottitis. If another accessory infection is being fought or there are certain medical problems it may fail.
- Not being correctly vaccinated: that is, without the corresponding vaccination schedule.
Prevention
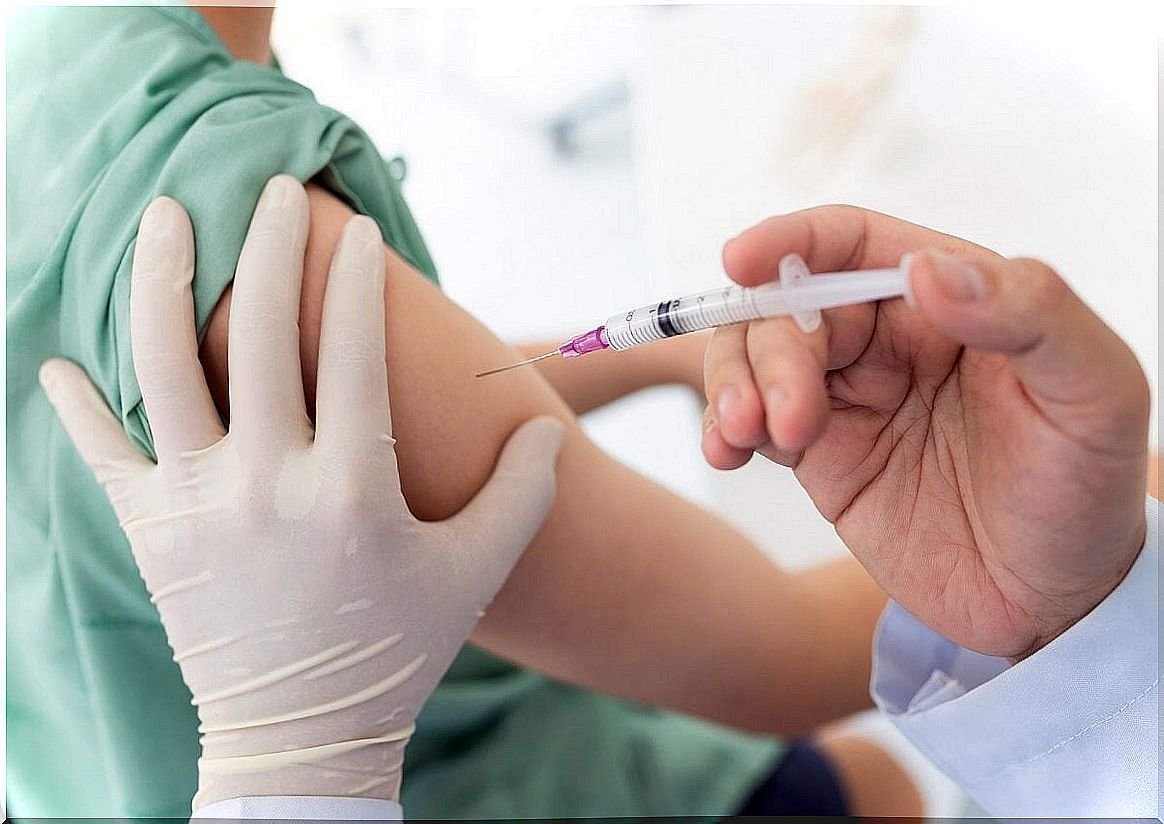
As indicated by the US National Library of Medicine, the Hib vaccine has killed the majority of epiglottitis cases in Western society. This procedure is usually performed in children under 5 years of age, as they are the most prone to severe infection.
On the other hand, the Hib bacteria are quite contagious, so if a family member has epiglottitis, all the individuals who share space with him are usually tested. Before confirming the diagnosis, it is essential not to share personal items and use disinfectant regularly.
Epiglottitis is prevented with vaccination
As with many other conditions, epiglottitis is a thing of the past in places with effective vaccination schedules. If the smallest people in the house or certain age groups at risk are correctly vaccinated, there should not be any type of problem or risk of suffering from this serious pathology.









